



LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) is a revolutionary technology that has transformed various industries with its remarkable capabilities. From mapping and surveying to environmental monitoring and autonomous vehicles, LiDAR plays a crucial role in generating precise and high-resolution data. In this article, we will explore the importance of LiDAR surveying, its accuracy, and its diverse applications that make it a game-changer in the world of technology and data acquisition.
LiDAR survey is a remote sensing technique that utilizes laser pulses to measure distances between the sensor and the Earth’s surface. By analyzing the time taken for the laser beams to bounce back after hitting objects or surfaces, LiDAR systems create highly accurate 3D point clouds. These point clouds can then be used to generate detailed digital elevation models (DEMs), topographic maps, and other spatial datasets.
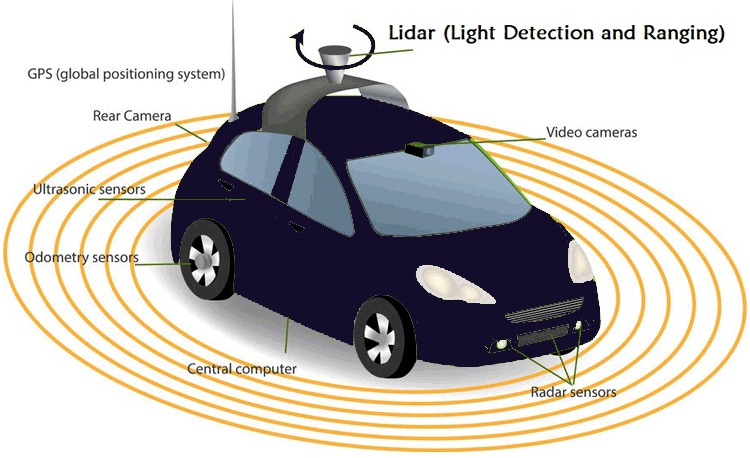
LiDAR survey holds immense significance across numerous industries due to its ability to provide precise and comprehensive data about the Earth’s surface and its features. It facilitates efficient planning, design, and decision-making processes, thereby leading to cost savings and improved project outcomes. Whether it’s for infrastructure development, forestry management, or disaster response, LiDAR surveying delivers unmatched value by offering a wealth of geospatial information.
LiDAR’s accuracy is a key factor that sets it apart from traditional surveying methods. It can achieve centimeter-level accuracy, making it ideal for projects that demand high precision. The accuracy of LiDAR survey data depends on factors such as the pulse repetition rate, scanning angle, and sensor calibration. Furthermore, ground control points (GCPs) are used to enhance accuracy by aligning LiDAR-derived data with other geospatial datasets.
The integration of LiDAR with drone technology has opened up new possibilities for data acquisition. LiDAR-equipped drones can capture data from challenging or inaccessible terrains, making it an ideal choice for mapping and surveying purposes. Some common uses of LiDAR drone surveying include precision agriculture, mining, environmental monitoring, and archaeological exploration.
Drone LiDAR surveys are known for their impressive accuracy, often achieving sub-centimeter level precision. This accuracy is a result of the drone’s ability to fly at low altitudes, enabling LiDAR sensors to capture data with high point densities. However, it’s essential to consider factors like the drone’s flight stability, sensor quality, and the quality of GCPs used to ensure optimal accuracy.
LiDAR assists in creating detailed 3D models of urban environments, aiding city planners and architects in designing sustainable and efficient infrastructure projects.
LiDAR is a valuable tool for assessing forest density, identifying tree species, and monitoring changes in vegetation over time, facilitating effective forest management and conservation efforts.
LiDAR-derived elevation data helps in assessing flood risks and modeling potential disaster scenarios, enabling authorities to develop robust mitigation plans.
LiDAR is employed to survey archaeological sites, revealing hidden features and ancient landscapes that might otherwise remain undiscovered.
LiDAR’s real-time data collection and 3D mapping capabilities are instrumental in enabling safe and efficient navigation for autonomous vehicles and robotics.
LiDAR’s rapid data acquisition and large coverage area enable quick and efficient surveying, saving time and resources.
LiDAR is non-contact and can gather data from a distance, making it ideal for sensitive or hard-to-reach locations.
LiDAR produces detailed and accurate 3D models, enabling better decision-making and precise analysis.
LiDAR data can be easily integrated with other geospatial datasets, providing a holistic view of the environment.
LiDAR surveys can be classified into several categories based on their applications and data collection methods. Some common types include airborne LiDAR surveys (using fixed-wing aircraft or drones), terrestrial LiDAR surveys (using ground-based scanners), and bathymetric LiDAR surveys (for underwater mapping).
In India, LiDAR is gaining prominence in various sectors, including urban planning, agriculture, disaster management, and conservation. LiDAR data is helping Indian authorities in developing smart cities, precision agriculture practices, and monitoring environmental changes.
LiDAR survey technology has emerged as a transformative force across multiple industries, offering unmatched accuracy, efficiency, and versatility. Its applications, ranging from urban planning to archaeology and autonomous vehicles, continue to expand, showcasing its indispensability in the modern world. As LiDAR technology evolves further, it holds the promise of revolutionizing how we perceive and interact with our environment, driving progress and innovation for years to come.